Transverse mode
A transverse mode of a beam of electromagnetic radiation is a particular electromagnetic field pattern of radiation measured in a plane perpendicular (i.e., transverse) to the propagation direction of the beam. Transverse modes occur in radio waves and microwaves confined to a waveguide, and also in light waves in an optical fiber and in a laser's optical resonator.[1]
Transverse modes occur because of boundary conditions imposed on the wave by the waveguide. For example, a radio wave in a hollow metal waveguide must have zero tangential electric field amplitude at the walls of the waveguide, so the transverse pattern of the electric field of waves is restricted to those that fit between the walls. For this reason, the modes supported by a waveguide are quantized. The allowed modes can be found by solving Maxwell's equations for the boundary conditions of a given waveguide.
Contents |
Types of modes
Transverse modes are classified into different types:
- TE modes (Transverse Electric) no electric field in the direction of propagation.
- TM modes (Transverse Magnetic) no magnetic field in the direction of propagation.
- TEM modes (Transverse ElectroMagnetic) neither electric nor magnetic field in the direction of propagation.
- Hybrid modes nonzero electric and magnetic fields in the direction of propagation.
Some authors use an alternate notation;
- H modes have a magnetic field component in the direction of propagation. H modes are equivalent to TE modes.
- E modes have an electric field component in the direction of propagations. E modes are equivalent to TM modes.
In rectangular waveguide, rectangular mode numbers are designated by two suffix numbers attached to the mode type, such as TEmn, where m is the number of half-wavelengths across the width of the waveguide and n is the number of half-wavelengths across the height of the waveguide. In circular waveguide circular modes exist and here m is the number of half-wavelengths along a half-circumference and n is the number of half-wavelengths along a radius.[2]
Modes of hollow metallic waveguides filled with a homogeneous, isotropic material fall into the first two categories. Otherwise, except in cases of special symmetry, modes are generally of hybrid type. For example, light travelling in an optical fiber or other dielectric waveguide forms hybrid-type modes. The fiber modes are usually referred to as LP (linear polarization) modes, which refers to a scalar approximation for the field solution, treating it as if it contains only one transverse field component (this is accurate because of the low refractive index contrast in typical fibers), the transverse electromagnetic (TEM) type. A planar Fabry-Perot resonator or etalon can also exhibit linearly polarized TEM modes. A resonator employing curved mirrors cannot support a TEM mode. Such modes are almost always hybrid except for the special cases of the electric field polarized either radially or azimuthally. The former case corresponds to a TM mode, the latter to a TE mode. Equivalently, linear polarization and TEM modes are mutually exclusive for a Gaussian beam or any other beam with curved wavefronts.
Laser modes
In a laser with cylindrical symmetry, the transverse mode patterns are described by a combination of a Gaussian beam profile with a Laguerre polynomial. The modes are denoted TEMpl where p and l are integers labeling the radial and angular mode orders, respectively. The intensity at a point r,φ (in polar coordinates) from the centre of the mode is given by:
where ρ = 2r2/w2, and Lpl is the associate Laguerre polynomial of order p and index l. w is the spot size of the mode corresponding to the Gaussian beam radius.
With p=l=0, the TEM00 mode is the lowest order, or fundamental transverse mode of the laser resonator and has the same form as a Gaussian beam. The pattern has a single lobe, and has a constant phase across the mode. Modes with increasing p show concentric rings of intensity, and modes with increasing l show angularly distributed lobes. In general there are 2l(p+1) spots in the mode pattern (except for l=0). The TEM0i* mode, the so-called doughnut mode, is a special case consisting of a superposition of two TEM0i modes (i=1,2,3), rotated 360°/4i with respect to one another.
The overall size of the mode is determined by the Gaussian beam radius w, and this may increase or decrease with the propagation of the beam, however the modes preserve their general shape during propagation. Higher order modes are relatively larger compared to the TEM00 mode, and thus the fundamental Gaussian mode of a laser may be selected by placing an appropriately sized aperture in the laser cavity.
In many lasers, the symmetry of the optical resonator is restricted by polarizing elements such as Brewster's angle windows. In these lasers, transverse modes with rectangular symmetry are formed. These modes are designated TEMmn with m and n being the horizontal and vertical orders of the pattern. The intensity at point x,y is given by:
where Hm(x) is the mth order Hermite polynomial.
The TEM00 mode corresponds to exactly the same fundamental mode as in the cylindrical geometry. Modes with increasing m and n show lobes appearing in the horizontal and vertical directions, with in general (m+1)(n+1) lobes present in the pattern. As before, higher-order modes have a larger spatial extent than the 00 mode.
The phase of each lobe of a TEMmn is offset by π radians with respect to its horizontal or vertical neighbours. This is equivalent to the polarization of each lobe being flipped in direction.
The overall intensity profile of a laser's output may be made up from the superposition of any of the allowed transverse modes of the laser's cavity, though often it is desirable to operate only on the fundamental mode.
Modes in an optical fiber
The number of modes in an optical fiber distinguishes multi-mode optical fiber from single-mode optical fiber. To determine the number of modes in a step-index fiber, the V number needs to be determined: 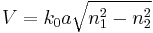 where
where 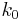 is the wavenumber,
is the wavenumber, 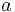 is the fiber's core radius, and
is the fiber's core radius, and 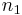 and
and 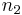 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, respectively. Fiber with a V-parameter of less than 2.405 only supports the fundamental mode (a hybrid mode), and is therefore a single-mode fiber whereas fiber with a higher V-parameter has multiple modes.[1]
are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, respectively. Fiber with a V-parameter of less than 2.405 only supports the fundamental mode (a hybrid mode), and is therefore a single-mode fiber whereas fiber with a higher V-parameter has multiple modes.[1]
Decomposition of field distributions into modes is useful because a large number of field amplitudes readings can be simplified into a much smaller number of mode amplitudes. Because these modes change over time according to a simple set of rules, it is also possible to anticipate future behavior of the field distribution. These simplifications of complex field distributions ease the signal processing requirements of fiber-optic communication systems.[2]
See also
References
- ^ "Transverse electromagnetic mode"
- ^ F. R. Connor, Wave Transmission, pp.52-53, London: Edward Arnold 1971 ISBN 0713132787.
![I_{pl} (\rho,\varphi) = I_0 \rho^l [L_p^l (\rho)]^2 \cos^2 (l\varphi) e^{-\rho}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/7193dbb89d57718d2b9402279fdf0d1c.png)
![I_{mn} (x,y) = I_0 \left[ \mbox{H}_m \left( \frac{ \sqrt{2} x}{w} \right) \exp \left( \frac{-x^2}{w^2} \right) \right]^2 \left[ \mbox{H}_n \left( \frac{ \sqrt{2} y}{w} \right) \exp \left( \frac{-y^2}{w^2} \right) \right]^2](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ae992d72f7a373b6ae1c4c593b2ee5bd.png)